Tire Pressure Monitoring System – TPMS

The Tire Pressure Monitoring System is a safety feature in vehicles designed to alert the driver when the tire pressure in one or more tires is significantly underinflated. Proper tire pressure is crucial for vehicle safety, fuel efficiency, and tire longevity. TPMS helps prevent accidents and breakdowns resulting from low tire pressure.
Here are the key components and functions of a typical TPMS:
- Sensors:
- Each tire is equipped with a sensor that monitors the tire pressure.
- The sensor can be an indirect system using the vehicle’s Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) sensors or a direct system with individual pressure sensors in each tire.
- Pressure Monitoring:
- The system continuously monitors the air pressure inside each tire in real-time.
- When the pressure drops below a predefined threshold (usually 25% less than the recommended pressure), the TPMS alerts the driver.
- Alerts to the Driver:
- TPMS alerts the driver through a dashboard warning light or a display on the instrument panel.
- The warning light typically looks like an exclamation mark inside a tire icon. The light may flash or remain illuminated, indicating the severity of the issue.
- Reset Procedure:
- After addressing low tire pressure (e.g., inflating the tires to the recommended levels), the system may require a reset to recognize the corrected pressure. This process varies among different vehicles.
- Types :
- Direct : Uses individual sensors inside each tire to measure pressure and send real-time data to the vehicle’s computer.
- Indirect : Utilizes the ABS sensors to monitor the rotational speed of each wheel. A sudden decrease in pressure causes changes in the wheel’s rotation, triggering the system to alert the driver.
- Benefits:
- Early Warning: TPMS helps drivers detect and address underinflated tires before they lead to unsafe driving conditions.
- Fuel Efficiency: Properly inflated tires contribute to better fuel efficiency.
- Tire Longevity: Maintaining optimal tire pressure extends the lifespan of tires.
- Regulations:
- Many countries, including the United States, Europe, and others, have regulations requiring the installation of TPMS in new vehicles.
Proper maintenance, including regular sensor battery checks and calibration, is essential for accurate and reliable performance. Drivers should follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for tire pressure and respond promptly to alerts to ensure safe driving conditions.
TPMS directly measures tire pressure using hardware sensors. In each wheel, most often on the inside of the valve, there is a battery-driven pressure sensor which transfers pressure information to a central control unit which reports it to the vehicle’s onboard computer. Some units also measure and alert temperatures of the tire as well. These systems can identify under-inflation for each individual tire. Although the systems vary in transmitting options, many TPMS products (both OEM and aftermarket) can display realtime, individual tire pressures whether the vehicle is moving or parked.
HONDA

HONDA HR-V

HONDA CIVIC

HONDA ODYSSEY

TOYOTA
TOYOTA YARIS
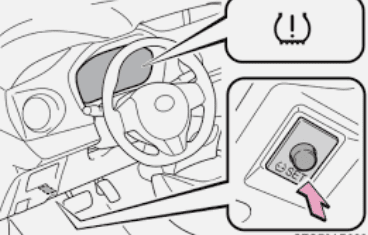
TOYOTA TACOMA
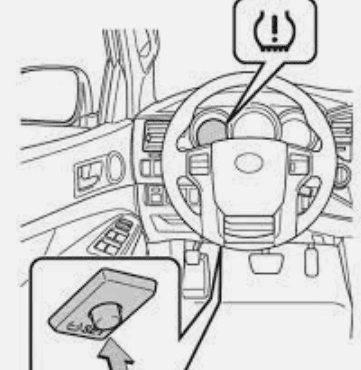
TOYOTA HIGHLANDER

HOME

