OBD2 CODES
P2000-P2BAE
P3000-P3F00
C0000-C3000
U0000-U3F00
OBD2 Codes meaning
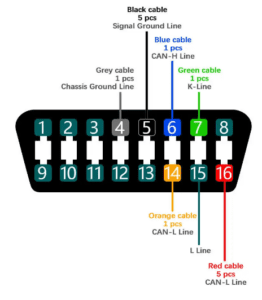
OBD-II (On-Board Diagnostics, Version 2) codes, often referred to as OBD2 codes or DTCs (Diagnostic Trouble Codes), are standardized codes used by vehicle computers (ECUs – Engine Control Units) to communicate information about the health and performance of various vehicle systems. When a problem or fault is detected by the vehicle’s onboard diagnostics system, it stores a specific OBD-II code to help mechanics and technicians diagnose and repair issues. These codes are primarily numeric and consist of five characters (e.g., P0420).
Here’s an overview of the main types of OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes:
- P-Codes (Powertrain Codes): These codes relate to the vehicle’s engine and transmission. They are the most common and provide information about issues with the engine, fuel and air metering, exhaust systems, and transmission.
- C-Codes (Chassis Codes): These codes pertain to various components in the chassis, such as the anti-lock brake system (ABS), stability control, and suspension.
- B-Codes (Body Codes): These codes cover issues related to body control modules, lighting, climate control, and other body-related functions.
- U-Codes (Network Communication Codes): These codes are related to network communication and data bus systems within the vehicle. They often indicate problems with wiring, connectors, or the network itself.
- Manufacturer-Specific Codes: In addition to the standardized P, C, B, and U codes, each automaker may have its own set of manufacturer-specific codes that offer more detailed information about their vehicles. These codes are often specific to a particular make and model of vehicle.
Here are some common OBD2 diagnostic trouble codes:
- P0300: Random/Multiple Cylinder Misfire Detected.
- P0420: Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (often related to the catalytic converter).
- P0171: System Too Lean (usually related to a fuel system issue).
- P0115: Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Circuit.
- C1234: Right Rear Wheel Speed Sensor Input Signal Missing.
- B0015: Driver’s Side Curtain Airbag Deployment Control Circuit (Body-related issue).
- U0100: Lost Communication with ECM/PCM A (Network communication issue).
When your vehicle’s check engine light (MIL – Malfunction Indicator Light) comes on, it means a fault has been detected, and the ECU has stored a corresponding OBD2 code. To diagnose the problem, you will need an OBD-II scanner or code reader to retrieve the codes. Once you have the codes, you can look them up in the vehicle’s owner’s manual or refer to online databases or repair guides to understand the issue and take appropriate action.
It’s important to note that while OBD2 codes provide a starting point for diagnostics, they don’t always pinpoint the exact problem. They indicate a system or component where the issue may exist, and further troubleshooting is often required to determine the root cause. If you are not comfortable diagnosing and repairing automotive issues, it’s advisable to consult a qualified mechanic or technician.
HOME
